The development that OPEC+ will witness will depend in large part on the development of the global system during the coming period, and whether it is favourable or opposed to the grouping of oil-exporting countries. Within this development, the results of the Russian special operation in Ukraine will play a significant role. Russia’s victory in this war will play the role of assistant and accelerator of the transitional process that the world order is going through, writes Abdullah bin Abdulmohsen Al-Faraj, Chairman Assistant for Scientific Affairs of the Center for Research & Knowledge Intercommunication.
Establishing the OPEC+ oil alliance
The establishment of the alliance reflects the stage that the World Order is going through, a transitional period, and at the same time, in some sense, reflects the world-wide geopolitical balance. The US 2008 mortgage crisis, which led to a financial and economic crisis with the United States at its epicentre, changed the economic balance in the world. After this crisis, China took the place of the United States as the locomotive that pulled behind it the global economy. Its GDP exceeded that of Britain and France in 2006 to become the fourth largest economy in the world; it took third place from Germany in 2007, and surpassed Japan in 2010. Within a short period, the matrix of major economies changed, and as a result, China became the second-largest economy in the world.
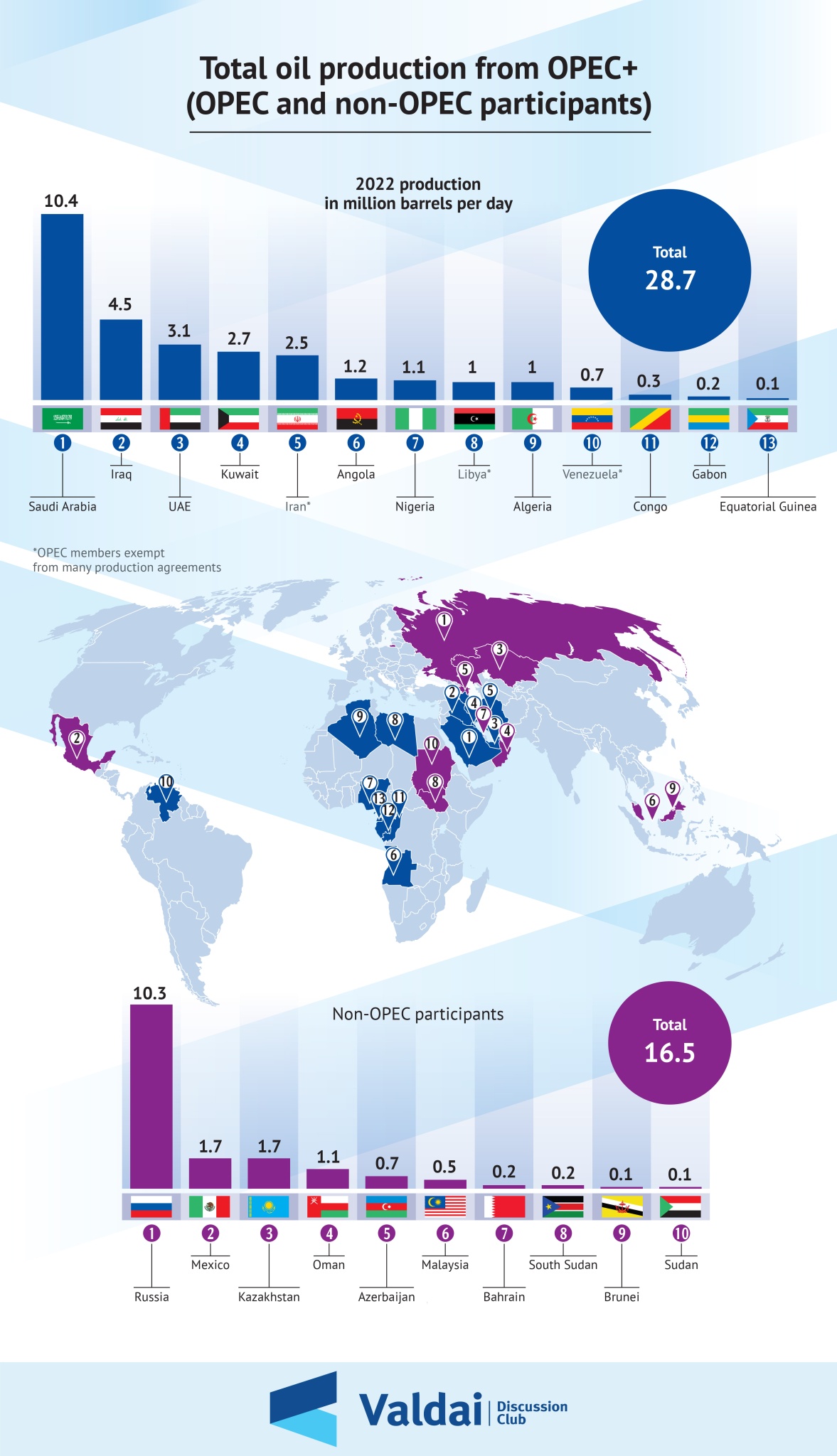
Infographic
Source: What is OPEC+ and how is it different from OPEC?
Table 1: The largest economies in the world during 2007-2010 by GDP, million USD
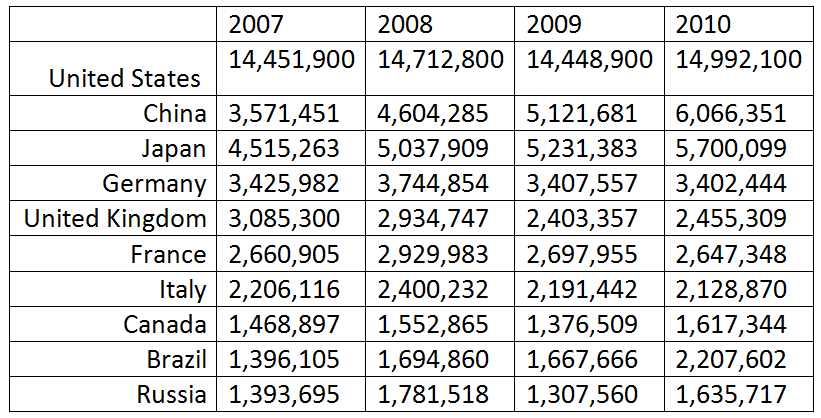
Source: countryeconomy.com
This led to the World Order entering a transitional period, in which China competed with the United States for global dominance, after the latter ended its role as the leader that no one could compete with in the unipolar system that followed the Cold War.
This development led to the emergence of three edges of a triangular World Order instead of one. As Mark Milley, former United States chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, pointed out, there are three great powers: the United States, China, and Russia. The last of these, thanks to the weapons it possesses, has been able to become a military force that the world takes into account.
It is worth noting that such a transitional phase takes place in the World Order once every hundred years.
The current World Order is experiencing a period similar to what it witnessed in the year 1914, when the United Kingdom was the world leader and the pound was the dominant global currency. But even in 1914, the United Kingdom did not wield the same power as it had previously.
It took two world wars to alter the map of global leadership, which finally changed after World War II.
The OPEC+ agreement and stability standards in the global market
Therefore, the establishment of OPEC+ in 2016 was part of what was previously mentioned, after the global system entered a transitional phase. OPEC+ reflects the change that has occurred in the matrix of major powers and the transformation of China and Russia into two vertices of the triangle of the global system along with the United States; the global system has become multi-sided, as Mark Milley pointed out.
On the other hand, the establishment of OPEC+ reflects the increase in energy supplies in the global market, after the discovery of shale gas in the United States, and the resulting decline in oil prices. Shale gas production has benefited from the rise in oil prices, and has gradually begun to take over OPEC’s share of the energy market. Therefore, in late 2014, OPEC decided to increase production, in order to replace shale gas and energy sources with high production costs. This is why oil prices declined in late 2014 and the following two years. If the average price of the OPEC basket in 2013 was $105.87 per barrel, then the average price reached $40.76. Therefore, the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia and Russia, specifically Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman and Russian President Vladimir Putin, decided to create an entity that would bring the two countries together and through which they could coordinate positions for promoting a fair oil price, which they called OPEC+. This group, as shown in the first Infographic, includes 10 countries outside OPEC: Russia and 9 other countries: Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Brunei, Malaysia, Kazakhstan, Mexico, Oman, Sudan, and South Sudan.
Table 2: Spot prices for the OPEC basket during 2013-2018
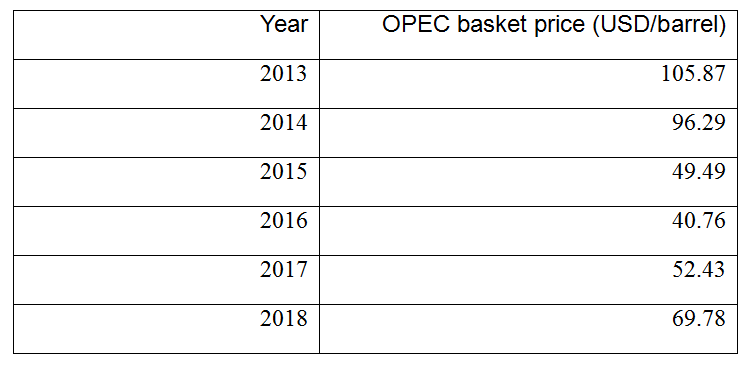
Source: The 55th annual report of the Saudi Arabian Monetary Agency for 2019.
Prospects for the development of OPEC+
OPEC+ gained greater geopolitical significance after Russia’s special military operation in Ukraine began on February 24, 2022, as a result of the world’s division over it. Despite the sanctions imposed by the West on Russia, OPEC+ continued to hold its meetings with the participation of Russia, which led to a state of uneasiness among anti-Russian circles, which wanted to isolate Russia from the rest of the world and render it a pariah state.
This sparked more and more interest in OPEC+, and many observers began to look forward to the meetings held by OPEC+ and the results of those meetings in order to stabilise global oil markets. They look with surprise at this consensus among OPEC+ members, including Russia, which the West wants to see isolated and helpless. This gave more geopolitical dimension to these meetings, the most recent of which was held early last June in Riyadh, in which an extension of the previously agreed-upon production cut was reached, as many factors played a role in making the decision, the most important of which are the following:
Oil prices are low and fluctuate around $80 per barrel for Brent.
Demand from China remains weak, and has not yet approached its pre-pandemic highs.
Increased production by countries outside the coalition, especially the United States, Canada and Brazil, leading to an increase in the supply of oil.
Many markets, especially the major Western industrial countries, are still suffering from inflation, which is expected to continue until the end of the year.
Therefore, the results of this meeting, in terms of geography, affect the interests of at least four continents: Asia, North America, South America, and Europe.
In terms of political geography, this meeting, like other meetings, affects the interests and nerves of decision makers in major countries. There is an attempt by huge oil-consuming and at the same time oil-producing countries, led by the United States, to render the OPEC+ meetings irrelevant. In this regard, sanctions imposed by the United States play a major role and have led to the capturing of the shares of other producers in the global oil market, the size of which amounts to 18 million barrels of oil per day, including the quotas of countries belonging to OPEC+.
Therefore, OPEC+ is called upon to continue coordination among its members in order to limit the impact of decisions taken by huge consumers, and which in the same time huge producers of energy, led by the United States. OPEC+ represents a challenge not only economically, but also geopolitically. This is because OPEC+ includes Russia.
The Valdai Discussion Club was established in 2004. It is named after Lake Valdai, which is located close to Veliky Novgorod, where the Club’s first meeting took place.
Please visit the firm link to site